As new research emerges, we learn how our neighbour, Jupiter, has more secrets than previously believed.
A team of scientists discovered that the edge of Jupiter’s huge magnetosphere has quite an effect on the planet. New faint aurora traits have been spotted, and scientists are now exploring all the possibilities. That includes the origin and how can we understand the phenomenon better.
Here is what you need to know.
Jupiter’s Auroral Feature Under Investigation
The discovery was made by the SwRI-led UV Spectrograph (UVS) orbiting Jupiter on NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
The faint aurora traits, characterized by some ring-like emissions, are pretty intriguing. A SwRI team released a paper discussing Jupiter’s features.
Dr Vincent Hue, the lead author of the research, explains:
“We think these newly discovered faint UV features originate millions of miles away from Jupiter, near the Jovian magnetosphere’s boundary with the solar wind.”
The solar wind is nothing but a supersonic flow of charged particles sent by the Sun. So, when they end up on Jupiter, they can influence its magnetosphere a lot in a way that scientists can’t figure out.
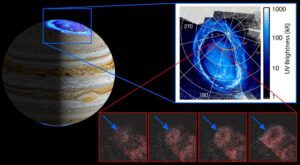
Juno’s bold mission
Juno’s primary goal is to examine Jupiter’s magnetosphere by calculating its auroras with the UVS tool.
Scientists were previously able to determine that most of our neighbour’s mighty auroras are produced by some internal processes. This approach was supported by the Hubble Space Telescope and Juno’s work.
Both our planet and Jupiter have a magnetic field that offers protection from the solar wind. We must understand that the more powerful the magnetic field, the biggest the magnetosphere.
For instance, Jupiter’s magnetic field is stronger than Earth, approximately 20,000 times. But that’s not all. Jupiter’s magnetic field can also generate a magnetosphere so big it starts to bounce the solar wind 2-4 million miles before it ends on Jupiter.
Although scientists still don’t know what processes make the new features, the Juno extended mission might be able to answer some questions.












Leave a Reply