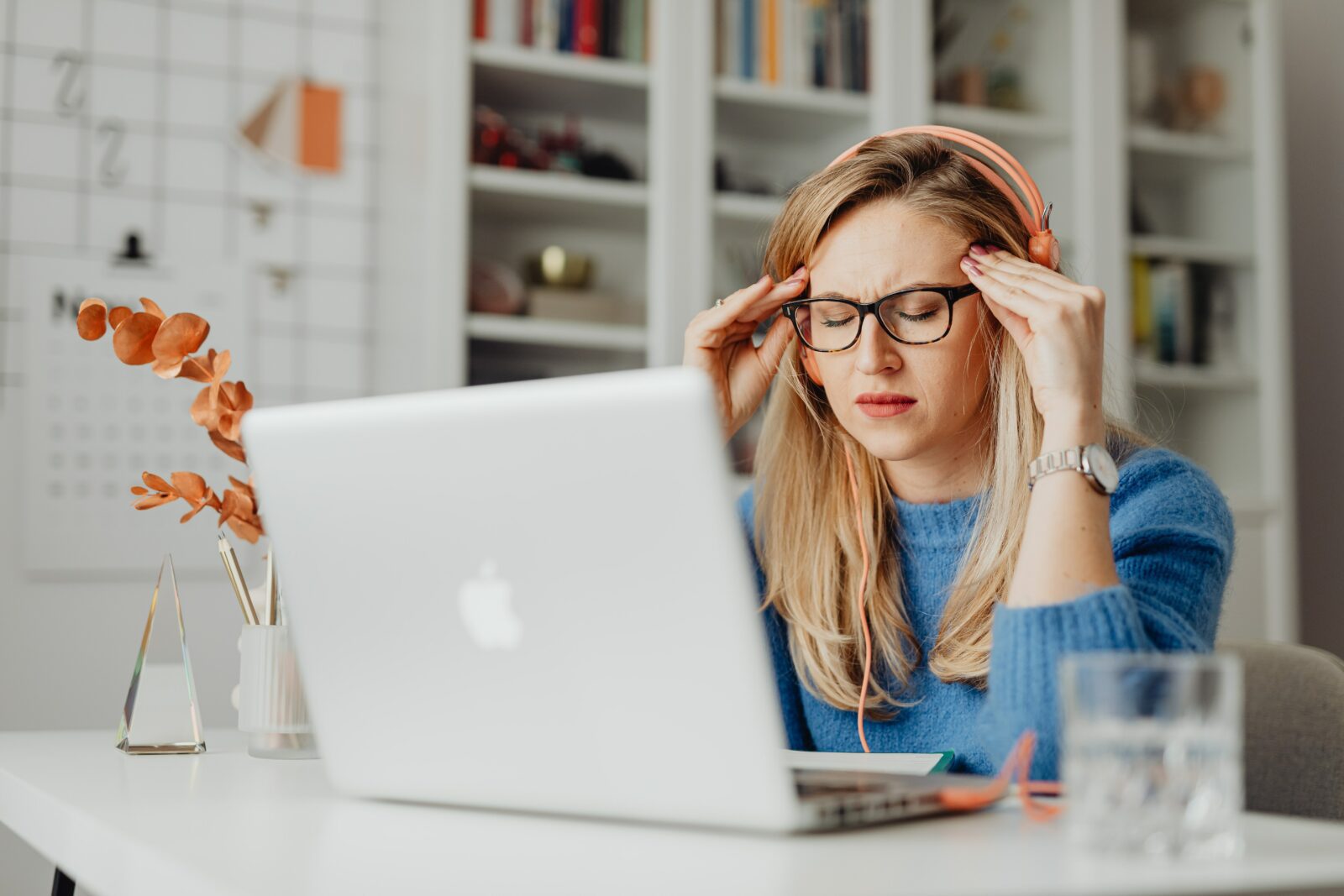
Stress causes inflammation. When stress hits the body, it triggers a hormone called cortisol, which leads to an inflammatory response. This inflammation is the body’s normal response to injury, sickness, and infection, and it may help the body recover. But chronic, low-grade inflammation can have harmful health effects, such as heart disease, obesity, and diabetes. This can explain why, after a stressful event, we’re prone to getting sick. The immune system becomes less responsive, and illness is easier to catch.
It’s also why stress can affect heart health. Cortisol, after all, also raises blood pressure and stimulates blood clotting. Higher blood pressure means more stress on the heart, which increases the likelihood it will suffer damage. All of these changes increase the risk of heart disease, one of the leading causes of death in Americans.
Stress can also affect your risk for a number of diseases, including hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes, depression, and autoimmune disorders. Stress can also cause inflammation, which is the immune response to infection. Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to diseases that attack our joints, like arthritis, or that damage our organs, like heart disease. Stress can lead to weight gain, through changes in appetite or changes in metabolism.
It can also lead to sleep problems, which can increase your risk for obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Stress can be responsible for or exacerbate mood swings, anxiety, depression, and substance abuse, all of which can be risk factors for heart disease. It’s a vicious cycle, and it’s one that can take a toll on everyone.
Some people are more resilient than others, but most of us feel it from time to time. Whether it’s work, relationships, or illness, stressful situations are unavoidable, and it’s vital to find ways to cope with them. Exercise, meditation, and therapy are all effective, but it’s always a good idea to consult your doctor if stress is affecting your health.










Leave a Reply